Keynote Speakers

Youmin Chen
Professor
Henan University, China
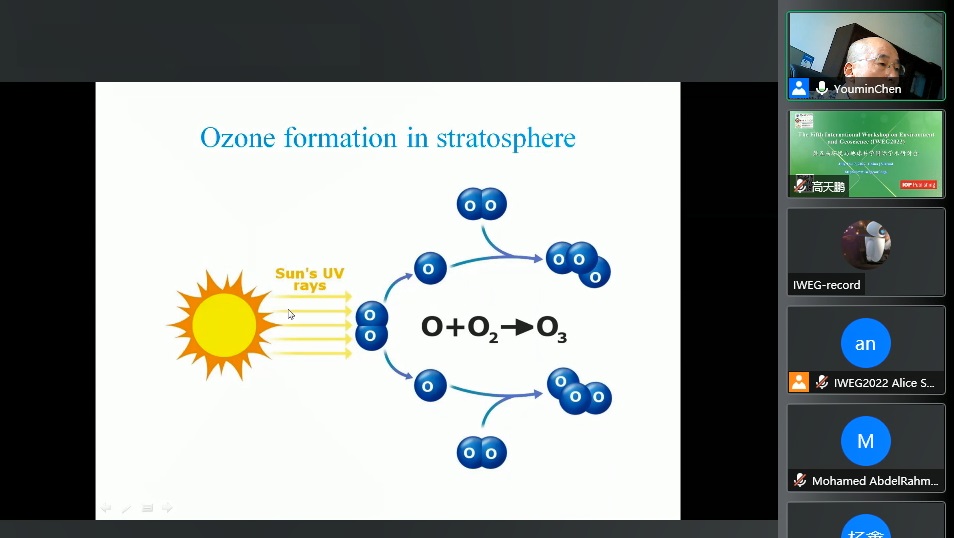
Abstract: In recent years, many extreme weather events occur frequently around the world, such as the extremely hot weather that spreaded throughout the Northern Hemisphere in the summer of 2022, and the unusually warm weather in winter. In addition, extreme precipitation events also occur more significantly, such as the heavy rain event in Zhengzhou on July 20, 2021. It is generally believed that these frequent weather and climate anomalies are caused by global warming. Is global warming the real culprit of extreme weather events? Using the regional climate model WRF, we selected an extreme precipitation process, namely, the Henan-758 rainstorm occurred in August 1975 in Henan Province, and carried out the conventional simulation first. Then, under the condition that other simulation conditions remain unchanged, the temperature element is artificially increased by 1.5 ° C and 2 ° C. This is the current threshold for controlling climate warming. Here this is equivalent to define a specific warming climate for our model simulation. WRF was again used to simulate the rainstorm Henan-758 but enploying the defined climate warming condition. The simulation results show that after climate warming, extreme precipitation will further strengthen, which will cause more serious natural disasters.

Chien-Yuan Chen
Professor
Department of Civil and Water Resources Engineering, National Chiayi University, Taiwan
Abstract: Climate change has caused numerous disasters around the world. It has also influenced the climate of Taiwan, with urban areas exhibiting a temperature increase by 1oC between 1998 and 2020. In this study, climate change and landslides in Taiwan were statistically analyzed. Cumulative annual precipitation in mountain watersheds in central Taiwan exhibit a declining trend and is lower than that in urban areas. The relatively few typhoons reduced the distribution of rainfall in mountain watersheds and fewer landslides. From 2017 to 2020, typhoon-induced rains caused fewer landslides than did other climate events such as the meiyu front, tropical low pressure, and southwesterly flow events. Three rainfall characteristics of landslide initiation were identified: high rainfall intensity over a short duration (<12 h), high-intensity and prolonged rainfall, and high cumulative rainfall over a long duration (>36 h). Combinations of warning models for landslides in cumulative rainfall–duration plots with rainfall intensity classification and mean rainfall intensity–duration plots with cumulative rainfall classification were presented. In recent (2018–2020) years, climate change has resulted in higher temperatures, less rainfall in mountain watersheds, and a lower rainfall threshold at which landslides are initiated by non-typhoon climate events. (Ref: Chen, H.-W.; Chen, C.-Y. Warning Models for Landslide and Channelized Debris Flow under Climate Change Conditions in Taiwan. Water 2022, 14, 695. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14050695).

Monzur Imteaz
Associate Professor
Head, Urban Environmental and Transport Systems;
School of Engineering, Swinburne University of Technology, Melbourne, Australia
Abstract: Contemporary focus of the whole world is to achieve a sustainable world reducing our exceedingly high ecological footprint through recycling and/or reusing different products, services and resources. For the countries who receive moderate to decent amount of rainfall, stormwater harvesting and reusing the stored stormwater is one of the most effective way of achieving water sustainability as it can significantly reduce the potable water demands for the urban areas. However, its effectiveness depends on many factors, such as amount of rainfall, stormwater demand, roof size and tank volume. In addition, cost of installing such tank and current potable water price play an important role on economic feasibility of such system. In fact, for many cities stormwater harvesting may not be economically feasible, unless current water price and associated policies are not altered. In many cases, installation and maintenance costs of stormwater harvesting may not be recoverable due to lower price of potable water. To establish this a thorough economic and payback period analysis is required. The talk will present few examples of such analyses in regard to stormwater harvesting, its associated costs and expected payback periods.

Shou Feng
Associate Professor
Harbin Engineering University, Harbin,China
Abstract: Remote sensing technology is an important technical means for human beings to perceive the world, and hyperspectral remote sensing technology has become the mainstream of current research. Hyperspectral image classification (HSIC) is a pixel-level classification task, which is mainly used for fine extraction and recognition of ground object information. HSIC is the basis for subsequent practical application tasks of hyperspectral images and has very important research significance, which is widely used in digital precision agriculture, environmental monitoring, national defense and military strategy and other fields. With the rapid development of artificial intelligence technology, many new hyperspectral image classification methods and algorithms have been proposed. Moreover, rapid advances in these methods have also promoted the application of associated algorithms and techniques to problems in many related fields. This keynote aims to report and cover the latest advances and trends about the Recent Advances in Hyperspectral Image Classification.

Yasir Al-Ani
Associate Professor
University of Anbar - Faculty of Engineering, Iraq
Abstract: The idea of sustainable development has encouraged society to recognize and value the significance of environmental factors in addition to the benefits and services the environment provides. In order to fulfill the needs of the current generation while still maintaining the sustainability of the environment for future generations, sustainable development aims to reduce the harmful effects of environmental degradation. The primary strategy for guaranteeing sustainable development is the inclusion of the environmental issue in local policy. Current speech will focus on the technologies related to wastewater treatment which follow the concept of sustainability in its application such as using solid wastes in the field of contamination control, and also using disposed materials in civil engineering field.